Chapter 5.2.4 / Carbon Cycle
Carbon Cycle
The purpose of this section is to provide an understanding of the carbon cycle and how changes in carbon stores impact climate change.
Professional Development for Educators
Carbon Cycle
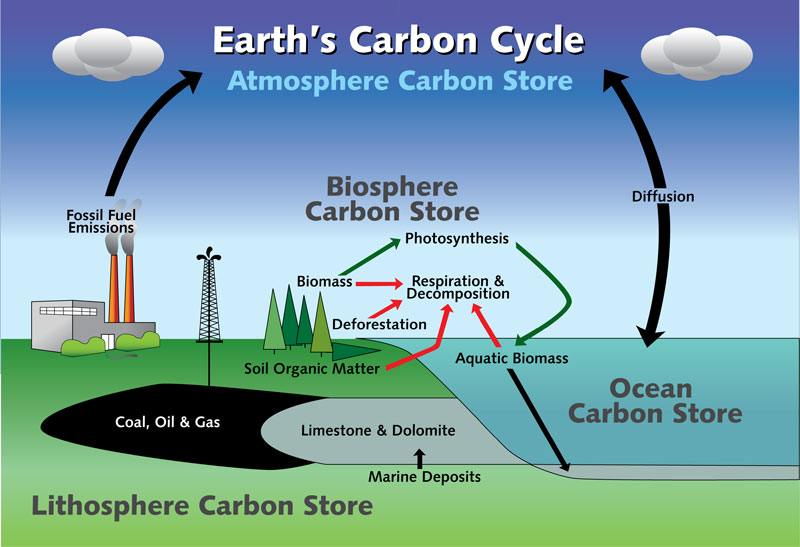
Source: http://www.dec.ny.gov/energy/76572.html
The earth has five spheres that are part of the carbon cycle:
- Atmosphere (envelope of gases surrounding earth)
- Hydrosphere (all bodies of water)
- Cryosphere (frozen part of earth’s surface)
- Lithosphere (rigid outer part of earth’s surface)
- Biosphere (regions of earth’s surface occupied by living organisms)
All living organisms are built of carbon compounds. It is the fundamental building block of life and an important component of many chemical processes.
In the atmosphere, carbon is present primarily as carbon dioxide (CO2), but also as other less abundant but climatically significant gases, such as methane (CH4).
Carbon is exchanged, or "cycled" among Earth's oceans, atmosphere, ecosystem, and geosphere. This movement of carbon, in its many forms, is the carbon cycle.
The video below is a simple explanation of the carbon cycle that students might enjoy.
Under In the Classroom below there is a classroom activity the provides a way for students to discover more about the carbon cycle.
These are key points for students to know about the carbon cycle:
- Life is fueled by carbon compounds.
- Animals and plants give off (release) carbon dioxide during respiration.
- Plants use carbon dioxide during photosynthesis and build new carbon compounds.
- CO2 is released by the burning of fossil fuels.
- The atmosphere and oceans are continuously exchanging CO2.
- The carbon cycle consists of reservoirs that store carbon. The storage reservoirs include the atmosphere, the oceans, vegetation, rocks, and soil.
- The carbon cycle also consists of the processes by which carbon moves between these reservoirs.
- If more carbon enters a pool than leaves it, that pool is considered a carbon sink. If more carbon leaves than enters, it is a carbon source.
- Carbon dioxide is a major player in the Earth’s energy balance. See 5.1 Climate System for more about the Earth's energy balance.
In the Classroom
Carbon Cycle
ACTIVITY (POGIL): The Carbon CycleYou can learn more about POGIL at: https://pogil.org/about
What is POGIL? from The POGIL Project on Vimeo.
More Information and Resources
Carbon Cycle
- The Department of Geosciences at Georgia State University has published a set of labs that may be helpful. Of particular interest are the following:
- Lab 4 The Carbon Cycle (Part 1) http://sites.gsu.edu/geog1112/lab-4-2/
- Lab 4 The Carbon Cycle (Part 2) http://sites.gsu.edu/geog1112/lab-4-the-carbon-cycle-part-2/
- TED Talk The Carbon Cycle (3:54 minutes) http://ed.ted.com/lessons/the-carbon-cycle-nathaniel-manning by Nathaniel Manning and Jill Johnston